
Sometimes, a biopsy is needed to rule out cancer. Some pyogenic granulomas disappear without treatment.
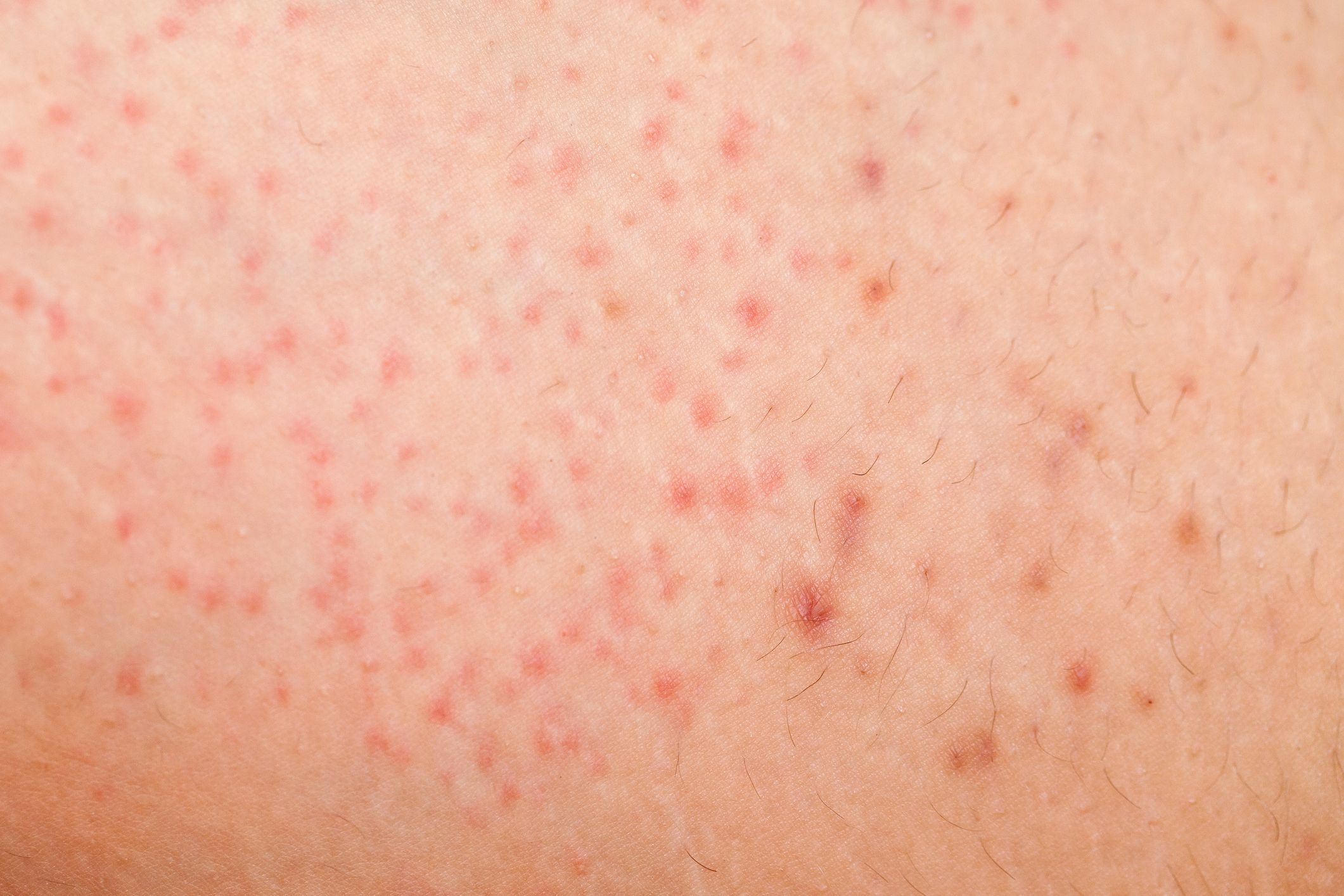
TWO PINPOINT RED DOTS ON SKIN SKIN
Pyogenic granulomas usually form after an injury to the skin and bleed easily.
Red, brown, or bluish-black, raised marks caused by excessive growth of capillaries (small blood vessels) and swelling. People with atypical moles should see a doctor for any changes that may indicate skin cancer. In addition, people with atypical moles should avoid sun exposure, since sunlight may accelerate changes in atypical moles. Treatment may include removal of any atypical mole that changes in color, shape or diameter. These types of moles may occur anywhere on the body. Atypical moles can be tan to dark brown, on a pink background. Larger than normal moles (more than a half inch across), atypical moles are not always round. Some benign moles may develop into skin cancer (melanoma). Most moles are benign and no treatment is necessary. Moles can change over time and often respond to hormonal changes. Most moles are dark brown or black, but some are skin-colored or yellowish. Moles can be flat or raised, smooth or rough, and some contain hair. Small skin marks caused by pigment-producing cells in the skin. But if the lipoma changes shape or you have symptoms, your healthcare provider may do a biopsy. Lipomas are more common in women and tend to appear on the forearms, torso, and back of the neck. Round or oval, easily movable lumps under the skin caused by fatty deposits. Other treatment may include surgical removal or injections of corticosteroids or fluorouracil. Treatment usually includes a skin biopsy to rule out skin cancer. Many feel they are a form of squamous cell carcinoma. They usually disappear after a couple of months, but may leave scars. These growths tend to appear on the face, forearm, or back of the hand. Round, flesh-colored growths that have a crater that contains a pasty material. Other treatment approaches may include surgery, laser, or silicone patches to further flatten the keloids. Injections of corticosteroid drugs may help to flatten the keloids. Keloids respond poorly to most treatment approaches. Keloids are more common in people with dark skin. Smooth, firm, raised, fibrous growths on the skin that form in wound sites.

Freckles are common in people with blond or red hair. Some internal dermoid tumors may even contain cartilage, bone fragments, and teeth.ĭermoid cysts may be removed surgically for cosmetic reasons.ĭarkened, flat spots that typically appear only on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are more common in women.ĭermatofibromas can be surgically removed if they become painful or itchy.Ī benign tumor which is made up of hairs, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands. They often occur on the legs and may itch. March 12, 2015.Small, firm, red or brown bumps caused by an accumulation of fibroblasts (soft tissue cells under the skin). In: Signs and Symptoms in Family Medicine. Approach to the adult patient with a bleeding diathesis. Physical abuse in children: Epidemiology and clinical manifestations.
Evaluation of adults with cutaneous lesions of vasculitis. Platelets, petechiae, and preservation of the vascular wall. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research 2014. Streptococcal pharyngitis (strep) (adult and pediatric). Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders Elsevier 2013. In: Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. Clinical approach to the patient with bleeding or bruising. Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders Elsevier 2015.
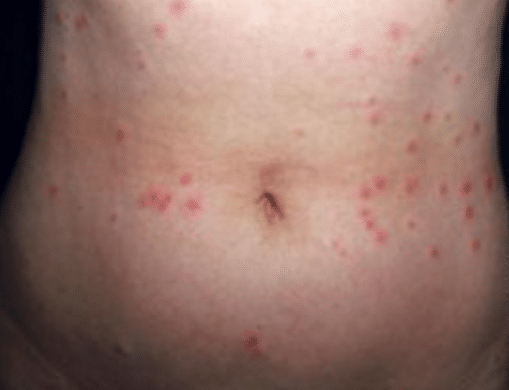
In: Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. The acutely ill patient with fever and rash.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
